Blue/Green deployments with AWS Lambda
July 27, 2020 • ☕️ 4 min read
Serverless computing is a cloud-based execution model that enables applications to be hosted as a service, without the need to maintain a server. Serverless & Lambda functions have become very popular in Cloud infrastructures from small to enterprise companies.
In this example will we are going to deploy a Symfony application (PHP) to AWS Lambda, using the following stack:
- Bref
- Serverless Framework + serverless-plugin-canary-deployments
On top of the classic PHP on AWS Lambda setup, this example will also configure AWS CloudWatch alerts and setup CodeDeploy to manage Blue/green canary deployments based on errors that are monitored using AWS CloudWatch.
Create our Symfony app:
symfony new bref-canary-deployments-demo
Install Bref:
composer req bref/bref
Learn more on how to setup a Symfony app here: https://bref.sh/docs/frameworks/symfony.html
I’m not going to focus on how to setup the Symfony application with Bref. If you have doubts or issues, you should follow the official documentation.
Deploy:
sls deploy
Under the wood, these steps have created the following infrastructure:
- AWS Lambda function with a custom PHP layer managed by Bref.
- An API Gateway
Until here, nothing new. This is a typical Serverless application, independent if you are deploying a PHP (customer layer) or a native AWS supported runtime (eg: NodeJS) you should relate to these steps and configurations.
Now we are going to setup the blue/gree deployments with gradually traffic shifting and automatic rollback.
Install serverless-plugin-canary-deployments:
npm i --save-dev serverless-plugin-canary-deployments
Enable serverless-plugin-canary-deployments on serverless framework configuration:
#serverless.yml
plugins:
- ./vendor/bref/bref
- serverless-plugin-canary-deployments
# ...Configure the gradually traffic shifting:
The new deploymentSettings will configure AWS CodeDeploy according to the defined type to deploy our Lambda
while the traffic is shifted in equal increments with an equal number of minutes between each increment.
In our example: Linear10PercentEvery1Minute - Shift 10 percent of the traffic, every 1 minute.
You can read more on the different Deployment Types here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/serverless-application-model/latest/developerguide/automating-updates-to-serverless-apps.html
#serverless.yml
functions:
website:
handler: public/index.php
timeout: 28 # in seconds (API Gateway has a timeout of 29 seconds)
layers:
- ${bref:layer.php-74-fpm}
events:
- http: 'ANY /'
- http: 'ANY /{proxy+}'
deploymentSettings: type: Linear10PercentEvery1Minute alias: Live alarms:
- ApiGateway5XXErrorAlarm
resources:
Resources:
ApiGateway5XXErrorAlarm:
Type: 'AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm'
Properties:
AlarmDescription: 'Api Gateway server-side errors captured'
Namespace: 'AWS/ApiGateway'
MetricName: 5XXError
Dimensions:
- Name: ApiName
Value: ${self:provider.stage}-${self:service}
Statistic: Sum
Period: 60
EvaluationPeriods: 1
Threshold: 1
ComparisonOperator: GreaterThanOrEqualToThresholdOn the following lines, we define and configure AWS CloudWatch to monitor our Lambda or API Gateway that AWS CodeDeploy will use as Threshold to decide if it should rollback or not the current deploy.
#serverless.yml
functions:
website:
handler: public/index.php
timeout: 28 # in seconds (API Gateway has a timeout of 29 seconds)
layers:
- ${bref:layer.php-74-fpm}
events:
- http: 'ANY /'
- http: 'ANY /{proxy+}'
deploymentSettings:
type: Linear10PercentEvery1Minute
alias: Live
alarms:
- ApiGateway5XXErrorAlarm
resources: Resources: ApiGateway5XXErrorAlarm: Type: 'AWS::CloudWatch::Alarm' Properties: AlarmDescription: 'Api Gateway server-side errors captured' Namespace: 'AWS/ApiGateway' MetricName: 5XXError Dimensions: - Name: ApiName Value: ${self:provider.stage}-${self:service} Statistic: Sum Period: 60 EvaluationPeriods: 1 Threshold: 1 ComparisonOperator: GreaterThanOrEqualToThreshold(Re)Deploy:
sls deploy
After you initiate a second deploy, it will create an additional set of resources on AWS:
- An Alarm on AWS CloudWatch
- An Application on CodeDeploy
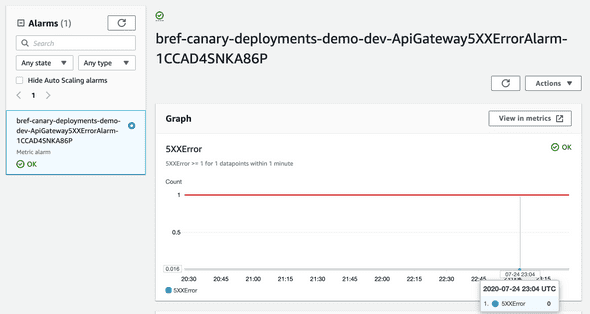
Important: We choose to setup our Alarm for API Gateway errors instead of using directly the lambda error metrics. This happen, because Lambda Errors don’t include the application exceptions/errors, because most of the time this is handle by the Framework (eg: Symfony) or even the language itself. Lambda errors will only take into account errors that break the runtime (eg: PHP). This is why, we decided to use API Gateway error metrics instead, but you can and should monitor both.
This new deploy will show up on AWS CodeDeploy:
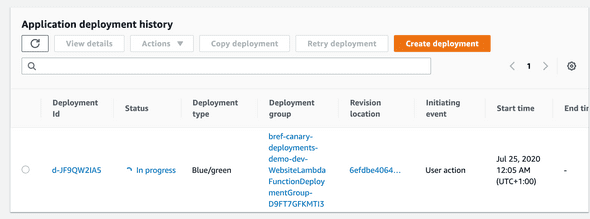
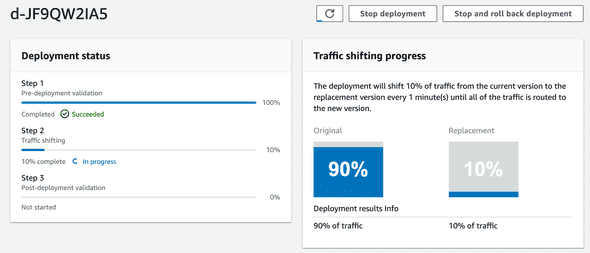
At the same time, we can also follow up on the traffic shifting progress and if we want, we can also manually Stop and rollback the deployment. During this moment if our API Gateway Alarm detect any error, the deployment will be automatically rollback by AWS CodeDeploy.
This process and configuration is a great way to deploy and monitor your Serverless applications but also to automate the rollback process on a CI/CD pipeline.
Tags: symfony • lambda • aws • php • deploy • deployment • bref • serverless-framework